文章
Miss Chen
2018年05月18日

Description: This perennial wildflower forms a rosette of ascending to spreading basal leaves. Individual basal leaves are 6-12" long and 2-4" across; they are dull green, elliptic to ovate in shape, smooth along their margins, and hairless. The basal leaves have parallel veins and they are longitudinally pleated. During some years, Wood's Bunchflower produces an unbranched flowering stalk about 3-6' tall. Relatively few alternate leaves are located along the lower-half of each stalk. The alternate leaves are similar to the basal leaves, except their bases are more slender, and they become much smaller in size while ascending the flower stalk. The bases of these alternate leaves partially sheath each stalk. Each central stalk is light green, terete, and pubescent, terminating in an inflorescence about 1-2' long.
This inflorescence consists of either a narrow raceme or elongated panicle of flowers. On each inflorescence, the upper flowers are perfect, while the lower flowers are staminate (male). The peduncle, lateral branches, and pedicels of the inflorescence are light green and pubescent, becoming dark brown with age. When lateral branches are present, they are 2-8" long and ascending to spreading (usually the former). The pedicels of the flowers are short (less than ½" long). Usually, there are narrow leafy bracts less than ½" long at the bases of the branches and pedicels. Perfect flowers are ½-¾" across, consisting of 6 widely spreading tepals, a small superior ovary, 6 stamens, and 3 styles. The narrow tepals are reddish brown (maroon) overall. The tepals have pairs of dark red glands at their bases, while toward the middle of each tepal there is often a transverse band of pale green or pale yellow. The ovary of each flower is light green, finely short-pubescent, and ovoid-conical in shape. Staminate flowers are the same as perfect flowers, except they lack an ovary and styles. The blooming period occurs from mid- to late summer for about 1 month.

Afterwards, the perfect flowers are replaced by 3-celled seed capsules that become, when they are mature, about ¾-1" long and about one-half as much across. These capsules have 3 longitudinal lobes with sharp ridges; they are usually sparsely pubescent and change color from green to dark brown. Each capsule usually contains only 0-3 seeds, although sometimes there are more. The tan-colored angular seeds are up to ½" long and ¼" across. The root system is rhizomatous. Sometimes vegetative offsets develop from the rhizomes.
Cultivation: The preference is dappled sunlight or light shade, moist conditions, and a rich soil that is often derived from glacial till. This wildflower has very few problems with insects pests and disease organisms. In any given year, entire colonies of plants may fail to produce flowers.
Range & Habitat: The native Wood's Bunchflower is restricted to central Illinois, where it is uncommon. In the past, this wildflower was state-listed as 'threatened,' but it was recently removed from this list as additional colonies of plants were discovered. Wood's Bunchflower is uncommon throughoutDistribution Map its range; it occurs primarily in Indiana, Illinois, and Missouri. Habitats include north- or east-facing wooded slopes along rivers, areas near streams in hilly woodlands, and shaded ravines. This wildflower is restricted to high quality deciduous woodlands where the original ground flora is still intact.
Faunal Associations: Almost nothing is known about floral-faunal relationships for Wood's Bunchflower. The maroon-colored flowers are probably cross-pollinated by flies and beetles. The caterpillars of a highly polyphagous moth, Xestia smithii (Smith's Dart), reportedly feed on this or a closely related species. Generally, Melanthium spp. (Bunchflowers) and the closely related Veratrum spp. (False Hellebores) have foliage, roots, and seeds that are considered highly poisonous to mammalian herbivores. There is some evidence that these plants are teratogenic, causing fatal birth defects in sheep. However, it is not uncommon to encounter specimens of Wood's Bunchflower that have been partially eaten by White-Tailed Deer.
Photographic Location: The photograph of the basal leaves was taken on a wooded slope facing a river in Vermilion County, Illinois, while the photograph of the seed capsules was taken in a hilly woodland near a stream in Coles County, Illinois.
Comments: Taxonomists are still divided regarding the classification of this wildflower: Some authorities refer to this species as Melanthium woodii (Wood's Bunchflower), as described here, while others refer to it as Veratrum woodii (Wood's False Hellebore). Perhaps additional genetic analysis will be helpful in resolving this conflict. The large basal leaves of Wood's Bunchflower are very conspicuous. This is one of the tallest wildflowers to bloom in woodlands during the summer, but the flowers are not produced reliably from year-to-year. The reason for this inconsistent flowering is not clear. Wood's Bunchflower is closely related to Melanthium virginicum (Virginia Bunchflower), but the latter species is found in damp sunny habitats. Virginia Bunchflower has white flowers, rather than maroon ones, and its leaves are more slender than those of Wood's Bunchflower. Both species are unusual in having conspicuous glands at the bases of their tepals.
This inflorescence consists of either a narrow raceme or elongated panicle of flowers. On each inflorescence, the upper flowers are perfect, while the lower flowers are staminate (male). The peduncle, lateral branches, and pedicels of the inflorescence are light green and pubescent, becoming dark brown with age. When lateral branches are present, they are 2-8" long and ascending to spreading (usually the former). The pedicels of the flowers are short (less than ½" long). Usually, there are narrow leafy bracts less than ½" long at the bases of the branches and pedicels. Perfect flowers are ½-¾" across, consisting of 6 widely spreading tepals, a small superior ovary, 6 stamens, and 3 styles. The narrow tepals are reddish brown (maroon) overall. The tepals have pairs of dark red glands at their bases, while toward the middle of each tepal there is often a transverse band of pale green or pale yellow. The ovary of each flower is light green, finely short-pubescent, and ovoid-conical in shape. Staminate flowers are the same as perfect flowers, except they lack an ovary and styles. The blooming period occurs from mid- to late summer for about 1 month.

Afterwards, the perfect flowers are replaced by 3-celled seed capsules that become, when they are mature, about ¾-1" long and about one-half as much across. These capsules have 3 longitudinal lobes with sharp ridges; they are usually sparsely pubescent and change color from green to dark brown. Each capsule usually contains only 0-3 seeds, although sometimes there are more. The tan-colored angular seeds are up to ½" long and ¼" across. The root system is rhizomatous. Sometimes vegetative offsets develop from the rhizomes.
Cultivation: The preference is dappled sunlight or light shade, moist conditions, and a rich soil that is often derived from glacial till. This wildflower has very few problems with insects pests and disease organisms. In any given year, entire colonies of plants may fail to produce flowers.
Range & Habitat: The native Wood's Bunchflower is restricted to central Illinois, where it is uncommon. In the past, this wildflower was state-listed as 'threatened,' but it was recently removed from this list as additional colonies of plants were discovered. Wood's Bunchflower is uncommon throughoutDistribution Map its range; it occurs primarily in Indiana, Illinois, and Missouri. Habitats include north- or east-facing wooded slopes along rivers, areas near streams in hilly woodlands, and shaded ravines. This wildflower is restricted to high quality deciduous woodlands where the original ground flora is still intact.
Faunal Associations: Almost nothing is known about floral-faunal relationships for Wood's Bunchflower. The maroon-colored flowers are probably cross-pollinated by flies and beetles. The caterpillars of a highly polyphagous moth, Xestia smithii (Smith's Dart), reportedly feed on this or a closely related species. Generally, Melanthium spp. (Bunchflowers) and the closely related Veratrum spp. (False Hellebores) have foliage, roots, and seeds that are considered highly poisonous to mammalian herbivores. There is some evidence that these plants are teratogenic, causing fatal birth defects in sheep. However, it is not uncommon to encounter specimens of Wood's Bunchflower that have been partially eaten by White-Tailed Deer.
Photographic Location: The photograph of the basal leaves was taken on a wooded slope facing a river in Vermilion County, Illinois, while the photograph of the seed capsules was taken in a hilly woodland near a stream in Coles County, Illinois.
Comments: Taxonomists are still divided regarding the classification of this wildflower: Some authorities refer to this species as Melanthium woodii (Wood's Bunchflower), as described here, while others refer to it as Veratrum woodii (Wood's False Hellebore). Perhaps additional genetic analysis will be helpful in resolving this conflict. The large basal leaves of Wood's Bunchflower are very conspicuous. This is one of the tallest wildflowers to bloom in woodlands during the summer, but the flowers are not produced reliably from year-to-year. The reason for this inconsistent flowering is not clear. Wood's Bunchflower is closely related to Melanthium virginicum (Virginia Bunchflower), but the latter species is found in damp sunny habitats. Virginia Bunchflower has white flowers, rather than maroon ones, and its leaves are more slender than those of Wood's Bunchflower. Both species are unusual in having conspicuous glands at the bases of their tepals.
0
0
文章
Miss Chen
2018年05月18日

Description: This perennial wildflower is 1-2½' tall, consisting of an erect unbranched stem and 1-2 whorls of leaves. Plants without flowers produce only a single whorl of leaves, while flowering plants produce 2 whorls of leaves. The central stem is medium green, terete, and woolly-pubescent to glabrous; it becomes more glabrous with age. In a flowering plant, the lower whorl of leaves occurs near the middle of the central stem; this whorl has 5-10 leaves that are 2½-5" long and ½-2" across. The upper whorl of leaves occurs underneath the inflorescence; this whorl has 3-5 leaves that are 2-4" long and ½-2" across. All of these leaves are elliptic to ovate in shape, smooth along their margins, and sessile. The upper leaf surface is medium green and glabrous, while the lower surface is pale green. Individual leaves have 3-5 parallel primary veins and a fine network of secondary veins.
The inflorescence consists of a sessile umbel of 3-9 flowers on pedicels about 1" long. These flowers are held either a little above or below the leaves when they are in bloom. Individual flowers are about 2/3" (16 mm.) across, consisting of 6 yellowish green tepals, 6 stamens, a 3-celled ovary, and 3 reddish purple to brown stigmata. The tepals are lanceolate in shape and recurved. The stigmata are large in size and recurved, spanning the width of each flower. The pedicels are light green and glabrous. The blooming period occurs from late spring to early summer, lasting about 1 month. Afterwards, the pedicels become more erect, holding the developing berries above the upper whorl of leaves. At maturity, these berries are dark purple, globoid, and about 1/4" to 1/3" (6-8 mm.) across. Each berry contains several seeds. The root system consists of a thick rhizome with fibrous roots. Small colonies of plants can develop from the rhizomes.
Cultivation: The preference is dappled sunlight to medium shade, moist to mesic conditions, and soil containing loam or sandy loam with decaying organic matter.

Range & Habitat: The native Indian Cucumber-Root is located in two counties of NE Illinois, where it is rare and state-listed as 'endangered' (see Distribution Map). Illinois lies along the western range-limit of this species. Habitats consist of rich mesic woodlands, edges of swamps, forested bogs, and at the bases of wooded dunes. In mesic areas, this wildflower is typically located in beech-maple woodlands, while in more swampy areas it is found near Red Maple, Black Ash, and other deciduous trees that prefer moist areas.
Faunal Associations: Very little is known about floral-faunal relationships for this species. Sometimes, such small rodents as the White-Footed Mouse and Woodland Deer Mouse eat the seeds and berries (Hamilton, 1941).

Photographic Location: The base of a wooded sand dune near the edge of a swamp at the Indiana Dunes National Lakeshore in NW Indiana.
Comments: The common name refers to the flavor of the rhizome, which is said to resemble the flavor of cucumbers. Because of the oversized stigmata, the flowers of Indian Cucumber-Root have an odd appearance. Non-flowering plants with a single whorl of leaves superficially resemble an orchid, Isotria verticillata (Large Whorled Pogonia). However, this orchid has been found only in southern Illinois, where Indian Cucumber-Root does not occur. In areas where their ranges overlap outside of the state, these two species can be distinguished by the differing patterns of their secondary veins.
The inflorescence consists of a sessile umbel of 3-9 flowers on pedicels about 1" long. These flowers are held either a little above or below the leaves when they are in bloom. Individual flowers are about 2/3" (16 mm.) across, consisting of 6 yellowish green tepals, 6 stamens, a 3-celled ovary, and 3 reddish purple to brown stigmata. The tepals are lanceolate in shape and recurved. The stigmata are large in size and recurved, spanning the width of each flower. The pedicels are light green and glabrous. The blooming period occurs from late spring to early summer, lasting about 1 month. Afterwards, the pedicels become more erect, holding the developing berries above the upper whorl of leaves. At maturity, these berries are dark purple, globoid, and about 1/4" to 1/3" (6-8 mm.) across. Each berry contains several seeds. The root system consists of a thick rhizome with fibrous roots. Small colonies of plants can develop from the rhizomes.
Cultivation: The preference is dappled sunlight to medium shade, moist to mesic conditions, and soil containing loam or sandy loam with decaying organic matter.

Range & Habitat: The native Indian Cucumber-Root is located in two counties of NE Illinois, where it is rare and state-listed as 'endangered' (see Distribution Map). Illinois lies along the western range-limit of this species. Habitats consist of rich mesic woodlands, edges of swamps, forested bogs, and at the bases of wooded dunes. In mesic areas, this wildflower is typically located in beech-maple woodlands, while in more swampy areas it is found near Red Maple, Black Ash, and other deciduous trees that prefer moist areas.
Faunal Associations: Very little is known about floral-faunal relationships for this species. Sometimes, such small rodents as the White-Footed Mouse and Woodland Deer Mouse eat the seeds and berries (Hamilton, 1941).

Photographic Location: The base of a wooded sand dune near the edge of a swamp at the Indiana Dunes National Lakeshore in NW Indiana.
Comments: The common name refers to the flavor of the rhizome, which is said to resemble the flavor of cucumbers. Because of the oversized stigmata, the flowers of Indian Cucumber-Root have an odd appearance. Non-flowering plants with a single whorl of leaves superficially resemble an orchid, Isotria verticillata (Large Whorled Pogonia). However, this orchid has been found only in southern Illinois, where Indian Cucumber-Root does not occur. In areas where their ranges overlap outside of the state, these two species can be distinguished by the differing patterns of their secondary veins.
0
0
文章
Miss Chen
2018年05月17日

Description: This herbaceous perennial wildflower is 3-8" tall. An infertile shoot usually consists of a single basal leaf, while a fertile shoot consists of a flowering stalk with 2 alternate leaves (less often, there are 3 leaves). Both basal and alternate leaves are similar in appearance, although the former have petioles up to 2" long. The leaves are up to 3" long and 2" across, smooth (entire) along their margins, and ovate-oblong to oval in shape. Leaf venation is parallel. The upper leaf surface is medium green and glabrous, while the lower leaf surface is pale green and finely pubescent. Unlike var. interius, the typical variety of Canada Mayflower has leaves without hairs. The base of each alternate leaf is clasping, sessile, or short-petioled. The central stalk is light to medium green, terete, and glabrous or hairy. At the apex of each flowering stalk, there is a short-cylindrical raceme of flowers about 1-2" long.
The flowers typically occur in pairs along the raceme on slender pedicels. Individual flowers have 4 white tepals, 4 stamens with white filaments and pale yellow anthers, and a white to greenish white pistil with a pair of knobby stigmata. The tepals are lanceolate and strongly recurved, fully exposing the reproductive organs. Each flower is a little less than ¼" (6 mm.) across. The blooming period occurs from late spring to early summer. The flowers are fragrant. During the summer, fertile flowers are replaced by globoid berries that are individually a little less than ¼" (6 mm.) across. At maturity, these berries are speckled pale red, and each berry typically contains 2 seeds. The root system is rhizomatous and fibrous. Vegetative colonies are often formed via the rhizomes. In a typical colony, infertile shoots usually outnumber flowering fertile shoots.

Cultivation: The preference is dappled sunlight to moderate shade, moist to slightly dry conditions, high humidity, and cool temperatures. This wildflower adapts to an acidic soil containing peat, sand, or rocky material (e.g., sandstone). It doesn't tolerate much competition from taller plants.
Range & Habitat: The native Canada Mayflower is uncommon in Illinois; it is restricted to the northern section of the state (see Distribution Map). Illinois lies at the southern range limit of this largely boreal species; it is more common further to the north in the Great Lakes region and further to the northeast in New England. The western variety of Canada Mayflower, var. interius, is far more common within the state than the more eastern typical variety. Habitats include sandy meadows, sandy thickets, sandy woodlands, north-facing wooded slopes, shaded bogs, and sandstone ledges along ravines in wooded areas. In Illinois, Canada Mayflower is associated with high quality natural areas.

Faunal Associations: The flowers are cross-pollinated by small bees, flies, and beetles. These floral visitors include Halictid bees (Halictus spp., Lasioglossum spp.), Andrenid bees (Andrena spp.), Syrphid flies, bee flies (Bombylius spp.), and Anthomyiid flies. No nectar is available to floral visitors. The bees collect pollen, while the flies and beetles feed on pollen. The foliage is consumed by the introduced Lilioceris lilii (Lily Leaf Beetle), while the larvae of a fly, Dasineura toronotensis, cause fusiform galls to develop on the roots. The berries are eaten by the Ruffed Grouse, White-Footed Mouse, and Eastern Chipmunk; these animals (particularly the Ruffed Grouse) help to spread the seeds of this plant into new areas.

Photographic Location: The photographs were taken at a sandstone ledge along a wooded ravine at the Fall Creek Gorge in west-central Indiana (also known as 'The Potholes'), and in a sandy thicket at the Irwin Prairie State Nature Preserve in NW Ohio.
Comments: This dainty wildflower resembles a dwarf Smilacina racemosa (False Solomon's Seal) or a dwarf Smilacina stellata (Starry Solomon's Plume). Unlike the preceding species, flowering stalks of Canada Mayflower typically have only 2 leaves. Another common name is False Lily-of-the-Valley. Among species of the Lily family, Canada Mayflower is very unusual in having only 4 tepals and 4 stamens per flower – other plants in this family typically have flowers with 6 tepals and 6 stamens.
The flowers typically occur in pairs along the raceme on slender pedicels. Individual flowers have 4 white tepals, 4 stamens with white filaments and pale yellow anthers, and a white to greenish white pistil with a pair of knobby stigmata. The tepals are lanceolate and strongly recurved, fully exposing the reproductive organs. Each flower is a little less than ¼" (6 mm.) across. The blooming period occurs from late spring to early summer. The flowers are fragrant. During the summer, fertile flowers are replaced by globoid berries that are individually a little less than ¼" (6 mm.) across. At maturity, these berries are speckled pale red, and each berry typically contains 2 seeds. The root system is rhizomatous and fibrous. Vegetative colonies are often formed via the rhizomes. In a typical colony, infertile shoots usually outnumber flowering fertile shoots.

Cultivation: The preference is dappled sunlight to moderate shade, moist to slightly dry conditions, high humidity, and cool temperatures. This wildflower adapts to an acidic soil containing peat, sand, or rocky material (e.g., sandstone). It doesn't tolerate much competition from taller plants.
Range & Habitat: The native Canada Mayflower is uncommon in Illinois; it is restricted to the northern section of the state (see Distribution Map). Illinois lies at the southern range limit of this largely boreal species; it is more common further to the north in the Great Lakes region and further to the northeast in New England. The western variety of Canada Mayflower, var. interius, is far more common within the state than the more eastern typical variety. Habitats include sandy meadows, sandy thickets, sandy woodlands, north-facing wooded slopes, shaded bogs, and sandstone ledges along ravines in wooded areas. In Illinois, Canada Mayflower is associated with high quality natural areas.

Faunal Associations: The flowers are cross-pollinated by small bees, flies, and beetles. These floral visitors include Halictid bees (Halictus spp., Lasioglossum spp.), Andrenid bees (Andrena spp.), Syrphid flies, bee flies (Bombylius spp.), and Anthomyiid flies. No nectar is available to floral visitors. The bees collect pollen, while the flies and beetles feed on pollen. The foliage is consumed by the introduced Lilioceris lilii (Lily Leaf Beetle), while the larvae of a fly, Dasineura toronotensis, cause fusiform galls to develop on the roots. The berries are eaten by the Ruffed Grouse, White-Footed Mouse, and Eastern Chipmunk; these animals (particularly the Ruffed Grouse) help to spread the seeds of this plant into new areas.

Photographic Location: The photographs were taken at a sandstone ledge along a wooded ravine at the Fall Creek Gorge in west-central Indiana (also known as 'The Potholes'), and in a sandy thicket at the Irwin Prairie State Nature Preserve in NW Ohio.
Comments: This dainty wildflower resembles a dwarf Smilacina racemosa (False Solomon's Seal) or a dwarf Smilacina stellata (Starry Solomon's Plume). Unlike the preceding species, flowering stalks of Canada Mayflower typically have only 2 leaves. Another common name is False Lily-of-the-Valley. Among species of the Lily family, Canada Mayflower is very unusual in having only 4 tepals and 4 stamens per flower – other plants in this family typically have flowers with 6 tepals and 6 stamens.
0
0
文章
Miss Chen
2018年05月17日

Description: This perennial plant is about 1½–2½' tall, branching occasionally. The stems are light green and densely covered with white hairs. The alternate leaves are up to 5½" long and 2" across; they are lanceolate to ovate, smooth along the margins, and sessile. The upper surface of each leaf is dark green, sparsely covered with short hairs, and pinnately veined; the lower surface is light green and densely covered with short white hairs. The lateral veins are conspicuous on both sides of the leaves. The flowers bloom near the apex of the stems. They occur individually from the axils of the leaves; their pedicels are short. Each flower is about ¼" across, consisting of a hairy green calyx with 5 linear-lanceolate teeth and a pale yellow corolla with 5 spreading lobes and a narrow throat. The tube of the corolla is no longer than the teeth of the calyx. The reproductive organs are hidden within the corolla. The blooming period occurs from mid-spring to early summer. Only a few flowers are in bloom at the same time. They are replaced by ovoid-globoid nutlets with an outer coat that is white, smooth, and hard. The root system consists of a taproot, which may send up more than one stem.
Cultivation: The preference is dappled sunlight during the spring and light to medium shade during the remainder of the year. The soil should be moist to slightly dry, fertile and loamy, containing abundant organic matter. The hard white seeds are difficult to germinate.
Range & Habitat: The native American Gromwell is scattered across Illinois; it is an uncommon plant (see Distribution Map). Populations of this species within the state have probably declined. Habitats include rich deciduous woodlands, wooded slopes, and shaded riverbanks. This conservative species prefers high quality woodlands where the original ground flora is largely intact.
Faunal Associations: The structure of the flowers suggests that the pollinators are long-tongued bees and butterflies. More specific information about floral-faunal relationships is currently unavailable.

Photographic Location: Toward the bottom of a moist wooded slope in Vermilion County, Illinois.
Comments: American Gromwell is one of the woodland wildflowers that blooms during the spring, but it is often overlooked and many field guides fail to describe it, probably because its flowers are not very showy. American Gromwell resembles Lithospermum officinale (European Gromwell) in its overall appearance. This latter species produces flowers in flat-headed cymes and its leaves are more slender. In contrast, American Gromwell produces individual flowers from the axils of the leaves. Another European species, Buglossoides arvense (Corn Gromwell), produces individual flowers from the axils of the leaves, but these flowers are bright white and its leaves are smaller in size. Corn Gromwell produces nutlets that are brown and wrinkled, rather than smooth and white. Other Lithospermum spp. in Illinois are native prairie plants that also produce flowers in flat-headed cymes. The flowers of these latter species have longer corollas that are a brilliant yellow or orange-yellow.
Cultivation: The preference is dappled sunlight during the spring and light to medium shade during the remainder of the year. The soil should be moist to slightly dry, fertile and loamy, containing abundant organic matter. The hard white seeds are difficult to germinate.
Range & Habitat: The native American Gromwell is scattered across Illinois; it is an uncommon plant (see Distribution Map). Populations of this species within the state have probably declined. Habitats include rich deciduous woodlands, wooded slopes, and shaded riverbanks. This conservative species prefers high quality woodlands where the original ground flora is largely intact.
Faunal Associations: The structure of the flowers suggests that the pollinators are long-tongued bees and butterflies. More specific information about floral-faunal relationships is currently unavailable.

Photographic Location: Toward the bottom of a moist wooded slope in Vermilion County, Illinois.
Comments: American Gromwell is one of the woodland wildflowers that blooms during the spring, but it is often overlooked and many field guides fail to describe it, probably because its flowers are not very showy. American Gromwell resembles Lithospermum officinale (European Gromwell) in its overall appearance. This latter species produces flowers in flat-headed cymes and its leaves are more slender. In contrast, American Gromwell produces individual flowers from the axils of the leaves. Another European species, Buglossoides arvense (Corn Gromwell), produces individual flowers from the axils of the leaves, but these flowers are bright white and its leaves are smaller in size. Corn Gromwell produces nutlets that are brown and wrinkled, rather than smooth and white. Other Lithospermum spp. in Illinois are native prairie plants that also produce flowers in flat-headed cymes. The flowers of these latter species have longer corollas that are a brilliant yellow or orange-yellow.
0
0
文章
Miss Chen
2018年05月17日

Description: This herbaceous perennial plant is about 2-4' tall and either branched or unbranched. The stems are light to medium green and abundantly covered with stiff white hairs that have the capacity to sting when they are rubbed against. The lower to middle leaves are alternate, while the upper leaves are opposite. These leaves are up to 6" long and 4" across; they are medium to dark green, ovate-cordate to oval-ovate in shape, and coarsely serrated or serrated-crenate. Young leaves are densely hairy and wrinkled in appearance, while older leaves become less hairy and wrinkled with age. Leaf venation is pinnate. The petioles are up to 4" long and abundantly covered with stinging hairs, like the stems. The leaves may have a few stinging hairs as well, particularly along the central veins of their undersides. Some plants have a tendency to loose many of their stinging hairs as the season progresses. Individual plants are either monoecious (separate male and female flowers on the same plant) or unisexual.
The male flowers occur in branching cymes from the axils of the leaves. These cymes spread outward from the stem and they are about the same length as the petioles of the leaves. Each male flower is greenish white to white and less than 1/8" (3 mm.) across, consisting of 5 narrow sepals, 5 stamens, and no petals. The female flowers occur in branching cymes toward the apex of the plant. These cymes are erect to spreading and 4" or more in length. Each female flower is more or less green and about 1/8" (3 mm.) across, consisting of 4 sepals of unequal size (2 large and 2 small) and an ovary with a long style. The blooming period usually occurs during mid- to late summer. The flowers are wind-pollinated. Each female flower is replaced by a small dry fruit that is curved and ovoid in shape. This plant often forms colonies of variable size.
Cultivation: The preference is partial sun to medium shade, moist conditions, and a fertile loamy soil with abundant organic matter. Because of its stinging hairs and tendency to spread, you probably would not want to cultivate this plant near the house, except possibly as a privacy barrier.
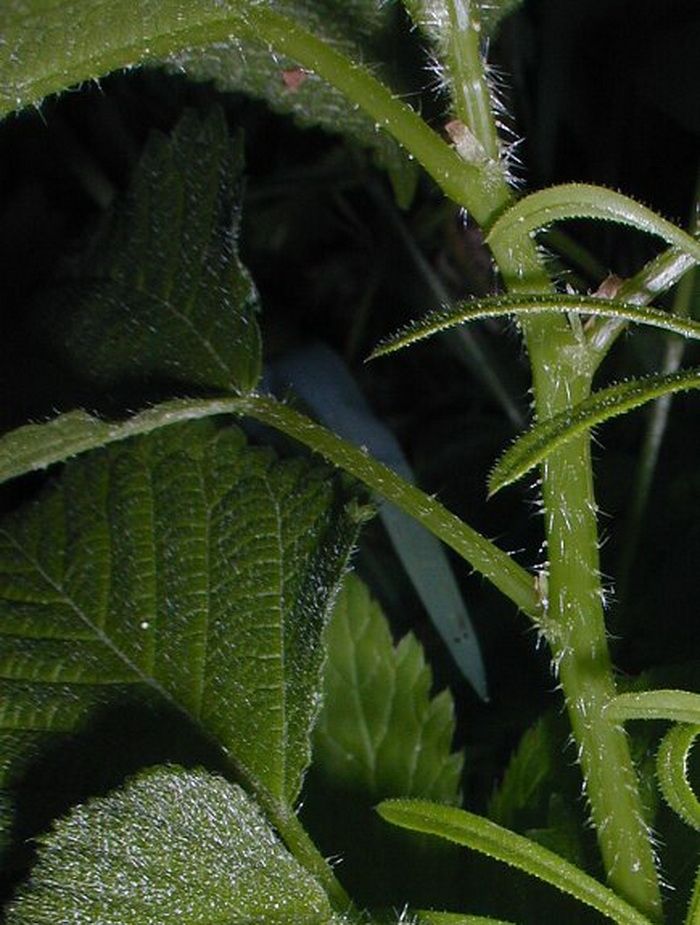

Range & Habitat: The native Wood Nettle is common in central and northern Illinois, but it is uncommon or absent in parts of southern Illinois (see Distribution Map). Habitats include moist floodplain woodlands, moist bottomland woodlands, mesic woodlands, shady seeps, and other moist places in wooded areas. Various deciduous trees (e.g., elms, maples, or sycamore) dominate the habitats where the Wood Nettle occurs.
Faunal Associations: The caterpillars of the following butterflies feed on the foliage: Polygonia comma (Comma), Polygonia interrogationis (Question Mark), and Vanessa atalanta (Red Admiral). Other insect feeders include caterpillars of the moths Bomolocha edictalis (Large Bomolocha) and Bomolocha sordidula (Sordid Bomolocha), leaf-mining larvae of the fly Agromyza subnigripes, and the stink bug Proxys punctulatus. White-tailed Deer also browse on the foliage of Wood Nettle occasionally, notwithstanding the stinging hairs. When this plant forms dense colonies in wooded areas, it provides valuable cover for wildlife.

Photographic Location: A floodplain woodland in Vermilion County, Illinois. The Wood Nettle in the photographs wasn't in bloom.
Comments: This native plant is often mistaken for the introduced Urtica dioica (Stinging Nettle). Both species have stinging hairs and a similar appearance. However, the Wood Nettle has some alternate leaves, while Stinging Nettle has pairs of opposite leaves only. There are also differences in the characteristics of their flowers. Another similar species, Boehmeria cylindrica (False Nettle), also has opposite leaves, but it lacks stinging hairs altogether. Like other members of the Nettle family, the Wood Nettle lacks showy flowers because they are wind-pollinated, rather than pollinated by insects. Some people may regard this species as an undesirable woodland weed because of its stinging hairs and unassuming appearance, but it is an important host plant of some native butterflies.
The male flowers occur in branching cymes from the axils of the leaves. These cymes spread outward from the stem and they are about the same length as the petioles of the leaves. Each male flower is greenish white to white and less than 1/8" (3 mm.) across, consisting of 5 narrow sepals, 5 stamens, and no petals. The female flowers occur in branching cymes toward the apex of the plant. These cymes are erect to spreading and 4" or more in length. Each female flower is more or less green and about 1/8" (3 mm.) across, consisting of 4 sepals of unequal size (2 large and 2 small) and an ovary with a long style. The blooming period usually occurs during mid- to late summer. The flowers are wind-pollinated. Each female flower is replaced by a small dry fruit that is curved and ovoid in shape. This plant often forms colonies of variable size.
Cultivation: The preference is partial sun to medium shade, moist conditions, and a fertile loamy soil with abundant organic matter. Because of its stinging hairs and tendency to spread, you probably would not want to cultivate this plant near the house, except possibly as a privacy barrier.

Range & Habitat: The native Wood Nettle is common in central and northern Illinois, but it is uncommon or absent in parts of southern Illinois (see Distribution Map). Habitats include moist floodplain woodlands, moist bottomland woodlands, mesic woodlands, shady seeps, and other moist places in wooded areas. Various deciduous trees (e.g., elms, maples, or sycamore) dominate the habitats where the Wood Nettle occurs.
Faunal Associations: The caterpillars of the following butterflies feed on the foliage: Polygonia comma (Comma), Polygonia interrogationis (Question Mark), and Vanessa atalanta (Red Admiral). Other insect feeders include caterpillars of the moths Bomolocha edictalis (Large Bomolocha) and Bomolocha sordidula (Sordid Bomolocha), leaf-mining larvae of the fly Agromyza subnigripes, and the stink bug Proxys punctulatus. White-tailed Deer also browse on the foliage of Wood Nettle occasionally, notwithstanding the stinging hairs. When this plant forms dense colonies in wooded areas, it provides valuable cover for wildlife.

Photographic Location: A floodplain woodland in Vermilion County, Illinois. The Wood Nettle in the photographs wasn't in bloom.
Comments: This native plant is often mistaken for the introduced Urtica dioica (Stinging Nettle). Both species have stinging hairs and a similar appearance. However, the Wood Nettle has some alternate leaves, while Stinging Nettle has pairs of opposite leaves only. There are also differences in the characteristics of their flowers. Another similar species, Boehmeria cylindrica (False Nettle), also has opposite leaves, but it lacks stinging hairs altogether. Like other members of the Nettle family, the Wood Nettle lacks showy flowers because they are wind-pollinated, rather than pollinated by insects. Some people may regard this species as an undesirable woodland weed because of its stinging hairs and unassuming appearance, but it is an important host plant of some native butterflies.
0
0
文章
Miss Chen
2018年05月17日

Description: This herbaceous perennial plant is 1-2' tall, branching sparingly. The stems are green, reddish green, or reddish brown, and they are glabrous to slightly hairy. When they are present, these hairs are curved or appressed against their stems. The alternate leaves are up to 6" long and 4" across (excluding the petioles); they are pinnately divided into 3-5 leaflets or deep lobes, and their margins are coarsely toothed or shallowly cleft. The lobes of these leaves are relatively narrow and they have acute tips. The earliest leaves in spring have small patches of white that are scattered across their upper surfaces; these white patches don't develop in later leaves. The petioles are up to 2" long, light green to reddish brown, and glabrous to short-pubescent; they are flat or furrowed along their upper sides and convex below. Each upper stem terminates in 1 or 2 cymes of flowers. The flowering stalks (or peduncles) of these cymes are up to 4" long; they are terete and glabrous to short-pubescent.
The stalks terminate in dense cymes of flowers about 1-2" across; each cyme contains about 8-20 flowers. Each flower is about 8-12 mm. long, consisting of a corolla with 5 lobes, a hairy green calyx with 5 linear teeth, 5 stamens, and a slender white style that is divided at its tip. The corolla is white, pink, or light lavender; its oblong lobes spread apart only slightly when the flower is fully open. The stamens are strongly exerted from the corolla and quite conspicuous; they have hairy white filaments and brownish anthers. The pedicels of the flowers are up to 12 mm. (½") in length; they are terete and glabrous to short-pubescent. The blooming period occurs during late spring to early summer, lasting about 3-4 weeks; some plants may bloom a little earlier or later than this. Each flower is replaced by a seed capsule that splits open to release its seeds. The root system consists of a tuft of fibrous roots and rhizomes. Occasionally, this plant forms colonies.

Cultivation: The preference is partial sun to light shade, moist to dry-mesic conditions, and a rich loamy soil with decaying leaves. This plant can be cultivated in gardens where there is some shade from deciduous trees.
Range & Habitat: The native Virginia Waterleaf is occasional to locally common in central and northern Illinois, while in southern Illinois it is uncommon or absent (see Distribution Map). Habitats include deciduous woodlands, savannas, areas along woodland paths, wooded slopes along rivers, bluffs, edges of clearings in wooded areas, and powerline clearances in wooded areas. This wildflower benefits from occasional disturbance if it removes excessive woody vegetation, and populations of this species decline in response to invasion from Garlic Mustard (Alliaria petiolata).

Faunal Associations: The nectar and pollen of the flowers attract bumblebees, long-horned bees (Synhalonia spp.), cuckoo bees (Nomada spp.), mason bees (Osmia spp.), Halictid bees (Lasioglossum spp., Augochlorella spp., etc.), Andrenid bees (Andrena spp.), and bee flies (Bombyliidae). An Andrenid bee, Andrena geranii, is a specialist pollinator of Hydrophyllum spp. Syrphid flies sometimes feed on the pollen of the flowers, but they are less effective at cross-pollination. The foliage is browsed by White-tailed Deer occasionally.
Photographic Location: Busey Woods in Urbana, Illinois.

Comments: This is probably the most common Hydrophyllum sp. in Illinois. Virginia Waterleaf has attractive flowers and foliage; it blooms a little later than most spring-blooming wildflowers in woodlands. The following characteristics distinguish this species from other Hydrophyllum spp. that occur in the state: 1) There are no curved appendages between the teeth of the calyx, 2) the stems are hairless, or they have lines of hairs that are curved or appressed against the stem, 3) the leaves are pinnately lobed and they are usually a little longer than wide, 4) the lobes of the corolla spread apart only a little, 5) the stamens and styles are longer than their corollas, and 6) the lobes of the leaves have acute tips. Other Hydrophyllum spp. have little appendages between the teeth of their calyxes, or they have stems with abundant spreading hairs, or they have palmately lobed leaves that are as wide as they are long, or the lobes of their corollas spread widely apart, or their stamens and styles are no longer than their corollas, or the lobes of their leaves have blunt tips. While this set of distinctions may sound complicated, it is usually easy to identify Virginia Waterleaf in the field.
The stalks terminate in dense cymes of flowers about 1-2" across; each cyme contains about 8-20 flowers. Each flower is about 8-12 mm. long, consisting of a corolla with 5 lobes, a hairy green calyx with 5 linear teeth, 5 stamens, and a slender white style that is divided at its tip. The corolla is white, pink, or light lavender; its oblong lobes spread apart only slightly when the flower is fully open. The stamens are strongly exerted from the corolla and quite conspicuous; they have hairy white filaments and brownish anthers. The pedicels of the flowers are up to 12 mm. (½") in length; they are terete and glabrous to short-pubescent. The blooming period occurs during late spring to early summer, lasting about 3-4 weeks; some plants may bloom a little earlier or later than this. Each flower is replaced by a seed capsule that splits open to release its seeds. The root system consists of a tuft of fibrous roots and rhizomes. Occasionally, this plant forms colonies.

Cultivation: The preference is partial sun to light shade, moist to dry-mesic conditions, and a rich loamy soil with decaying leaves. This plant can be cultivated in gardens where there is some shade from deciduous trees.
Range & Habitat: The native Virginia Waterleaf is occasional to locally common in central and northern Illinois, while in southern Illinois it is uncommon or absent (see Distribution Map). Habitats include deciduous woodlands, savannas, areas along woodland paths, wooded slopes along rivers, bluffs, edges of clearings in wooded areas, and powerline clearances in wooded areas. This wildflower benefits from occasional disturbance if it removes excessive woody vegetation, and populations of this species decline in response to invasion from Garlic Mustard (Alliaria petiolata).

Faunal Associations: The nectar and pollen of the flowers attract bumblebees, long-horned bees (Synhalonia spp.), cuckoo bees (Nomada spp.), mason bees (Osmia spp.), Halictid bees (Lasioglossum spp., Augochlorella spp., etc.), Andrenid bees (Andrena spp.), and bee flies (Bombyliidae). An Andrenid bee, Andrena geranii, is a specialist pollinator of Hydrophyllum spp. Syrphid flies sometimes feed on the pollen of the flowers, but they are less effective at cross-pollination. The foliage is browsed by White-tailed Deer occasionally.
Photographic Location: Busey Woods in Urbana, Illinois.

Comments: This is probably the most common Hydrophyllum sp. in Illinois. Virginia Waterleaf has attractive flowers and foliage; it blooms a little later than most spring-blooming wildflowers in woodlands. The following characteristics distinguish this species from other Hydrophyllum spp. that occur in the state: 1) There are no curved appendages between the teeth of the calyx, 2) the stems are hairless, or they have lines of hairs that are curved or appressed against the stem, 3) the leaves are pinnately lobed and they are usually a little longer than wide, 4) the lobes of the corolla spread apart only a little, 5) the stamens and styles are longer than their corollas, and 6) the lobes of the leaves have acute tips. Other Hydrophyllum spp. have little appendages between the teeth of their calyxes, or they have stems with abundant spreading hairs, or they have palmately lobed leaves that are as wide as they are long, or the lobes of their corollas spread widely apart, or their stamens and styles are no longer than their corollas, or the lobes of their leaves have blunt tips. While this set of distinctions may sound complicated, it is usually easy to identify Virginia Waterleaf in the field.
0
0
文章
权问薇
2018年05月17日


健胃消食片
健胃消食片是咱们平时促进肠胃消化的药,呈酸性,可以制成酸性肥,为了花能更好的吸收,一般泡成肥水来用
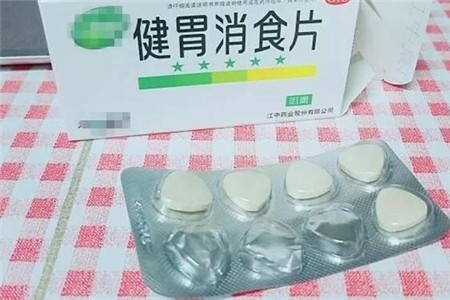
1、泡水溶解
2-3粒消食片兑500毫升清水,摇一摇使药片快速溶解
2、发酵
放在有阳光的地方发酵,现在的气温,大概2-3天就发酵好了(闻到酸酸的酒气),偶尔开下盖子敞气
3、使用
发酵好的肥水要兑清水,肥水:清水=1:10,浇土里或者擦拭叶子都行
4、花开更多
消食片肥水里面有丰富的营养菌、微量元素,是非常好的酸性复合肥,可以促花、催花
维生素C
维生素C几乎家家都有,都说是美容养颜,但总是忘了吃,有些都过期了,赶紧拿来养花吧

1、兑水浇花
维生素C很好溶解,特别是VC泡腾片,一片可以快速冲一杯
2、浇花
1粒维生素C冲1000毫升的水就可以直接浇花了,适用于月季、栀子、茶花、米兰等喜酸的花
3、减少黄叶,延长花期
VC可以抗氧化,帮助植物抵抗空气中的氯气,1个月浇上2次左右,可以延长花期,保护植物减少氧化~
维生素B12
花动不动就黄叶枯萎,多半是根出了问题,根肥才能叶壮,所以先把根养好,喂它吃点维生素B12吧

1、碾碎拌花土
将2-3粒维生素B12碾碎,均匀拌在盆土里,已经栽好的可以在5厘米深的地方埋一圈
2、浇水
1-2粒维生素B12兑1000毫升水,可以直接来浇花
3、养根、防虫
VB12可以提高根系的抵抗力,根壮了开花自然多。不仅如此,虫子非常讨厌它的气味,所以用它来浇花虫子都绕道走啦
阿司匹林
阿司匹林也是大部分家中的常备药,头疼什么的都需要它,大家可能还不知道,它也能养花~

1、兑水浇花
1-2粒阿司匹林先碾碎,然后兑上1升的清水,摇匀就可以浇花了
2、使花加速生长、提高抵抗力
阿司匹林里的水杨酸能够加快植物的生长速度,同时提高免疫力,不仅能当肥还能保健
紫药水
紫药水是家家必备,一有个磕磕碰碰就找它,你知道它还能用来养花吗?

1、治疗叶斑病
月季、栀子、发财树、绣球、君子兰等等很容易得叶斑病,难根治还传染,其实可以涂上紫药水来杀菌防传染
2、泡根杀菌
如果花烂根了,清理掉烂根后要及时消炎杀菌,也可以放在紫药水里泡上5-10分钟
达克宁
夏天来了,达克宁是不是又要开始轰炸了哈哈,感觉家里总是剩下半管子,放着都过期了,还不如拿来养花

1、治疗叶斑病
达克宁可以抑制真菌,防止传染,非常适合用在治疗花花草草的叶斑病、黄褐病
2、治疗烂根、防止深度腐烂
春夏季节,浇水稍有不慎花就烂根,如果是老桩花一换盆就死,这时候不用换盆也能救,先控水几天
控水后拔掉恢复不了的软叶、烂叶,根部稍微变的干燥就是好事
在根部涂抹达克宁,不要太多留点空隙给植物呼吸就行
一般轻微的根腐都可以用,不用眼睁睁看着花烂死啦
2
3
文章
Miss Chen
2018年05月16日

Description: This herbaceous perennial plant is about 1-2' tall, consisting of some basal leaves, branched stems with alternate leaves, and flowers. The basal leaves are up to 5" long and 5" across; they have long hairy petioles. Each basal leaf is palmately cleft into 3-5 lobes; these lobes are often divided again into smaller lobes. The alternate leaves are similar to the basal leaves, except they become smaller as they ascend the stems and their petioles are shorter. The upper leaves are more slender and divided into fewer lobes. The margins of the leaves are crenate or dentate. The upper surface of each leaf is medium to dark green and glabrous. The stems are light green, terete, and covered with long hairs; they are erect to ascending, rather than sprawling across the ground.
The upper stems terminate in loose clusters of flowers. Each flower is about 1/3" (8 mm.) across, consisting of 5-6 yellow petals, 5 light green sepals, a dense green cluster of pistils, and a ring of surrounding stamens with yellow anthers. The petals are oblong-elliptic and a little shorter than the sepals; the latter tend to hang downward while the flowers are blooming. The pedicels of the flowers are pubescent. The blooming period occurs from mid-spring to early summer and lasts about 1 month. Both sepals and petals are deciduous and they soon fall to the ground. The pistils become transformed into a dense cluster of flat-sided achenes with slender hooked beaks; this fruit is globoid in shape. Eventually, the fruit changes in color from green to nearly black. Each achene is about 2-3 mm. long. The root system consists of a cluster of fibrous roots and occasional rhizomes. Sometimes, small clonal colonies of plants are produced.

Cultivation: The preference is light to medium shade, wet to moist conditions, and soil with abundant organic material.
Range & Habitat: The native Hooked Buttercup is widely distributed in Illinois, but it is found only occasional in most areas (see Distribution Map). Habitats include damp depressions in upland woodlands, floodplain woodlands, shaded areas along streams, bottoms of rocky ravines, areas along woodland paths, swamps, forested bogs, and shady seeps. This species prefers damp woodlands and shaded wetlands.
Faunal Associations: The nectar of the flowers attracts primarily small bees. These include Cuckoo bees (Nomada spp.), Halictid bees (Augochlorella spp., Lasioglossum spp.), and Andrenid bees (Andrena spp.). Among vertebrate animals, the Wood Duck, Ruffed Grouse, and Wild Turkey feed on the seeds and foliage of Ranunculus spp. (Buttercups) in woodlands. The Eastern Chipmunk also eats the seeds of these plants. Hoofed mammalian herbivores usually avoid the consumption of buttercups because the toxic foliage contains a blistering agent that can irritate the mouth and gastrointestinal tract.
Photographic Location: Along a stream at the bottom of a rocky ravine at The Portland Arch in west-central Indiana.
Comments: This buttercup has achenes with unusually long hooked beaks; this provides its fruit with a slightly spiny appearance. While its foliage is reasonably attractive, the flowers are not very showy. Other similar buttercups include Ranunculus abortivus (Small-Flowered Buttercup) and Ranunculus pensylvanicus (Bristly Buttercup), which can be found in wet woodlands as well. Small-Flowered Buttercup has lower leaves that are kidney-shaped and lack lobes, while the palmately cleft leaves of Bristly Buttercup have more narrow lobes. The latter species also blooms later in the year (during the summer) than Hooked Buttercup. Other similar buttercups have larger flowers (at least ½" across) or their fruits (seedheads) are more elongated (ovoid or oblongoid) in shape.
The upper stems terminate in loose clusters of flowers. Each flower is about 1/3" (8 mm.) across, consisting of 5-6 yellow petals, 5 light green sepals, a dense green cluster of pistils, and a ring of surrounding stamens with yellow anthers. The petals are oblong-elliptic and a little shorter than the sepals; the latter tend to hang downward while the flowers are blooming. The pedicels of the flowers are pubescent. The blooming period occurs from mid-spring to early summer and lasts about 1 month. Both sepals and petals are deciduous and they soon fall to the ground. The pistils become transformed into a dense cluster of flat-sided achenes with slender hooked beaks; this fruit is globoid in shape. Eventually, the fruit changes in color from green to nearly black. Each achene is about 2-3 mm. long. The root system consists of a cluster of fibrous roots and occasional rhizomes. Sometimes, small clonal colonies of plants are produced.

Cultivation: The preference is light to medium shade, wet to moist conditions, and soil with abundant organic material.
Range & Habitat: The native Hooked Buttercup is widely distributed in Illinois, but it is found only occasional in most areas (see Distribution Map). Habitats include damp depressions in upland woodlands, floodplain woodlands, shaded areas along streams, bottoms of rocky ravines, areas along woodland paths, swamps, forested bogs, and shady seeps. This species prefers damp woodlands and shaded wetlands.
Faunal Associations: The nectar of the flowers attracts primarily small bees. These include Cuckoo bees (Nomada spp.), Halictid bees (Augochlorella spp., Lasioglossum spp.), and Andrenid bees (Andrena spp.). Among vertebrate animals, the Wood Duck, Ruffed Grouse, and Wild Turkey feed on the seeds and foliage of Ranunculus spp. (Buttercups) in woodlands. The Eastern Chipmunk also eats the seeds of these plants. Hoofed mammalian herbivores usually avoid the consumption of buttercups because the toxic foliage contains a blistering agent that can irritate the mouth and gastrointestinal tract.
Photographic Location: Along a stream at the bottom of a rocky ravine at The Portland Arch in west-central Indiana.
Comments: This buttercup has achenes with unusually long hooked beaks; this provides its fruit with a slightly spiny appearance. While its foliage is reasonably attractive, the flowers are not very showy. Other similar buttercups include Ranunculus abortivus (Small-Flowered Buttercup) and Ranunculus pensylvanicus (Bristly Buttercup), which can be found in wet woodlands as well. Small-Flowered Buttercup has lower leaves that are kidney-shaped and lack lobes, while the palmately cleft leaves of Bristly Buttercup have more narrow lobes. The latter species also blooms later in the year (during the summer) than Hooked Buttercup. Other similar buttercups have larger flowers (at least ½" across) or their fruits (seedheads) are more elongated (ovoid or oblongoid) in shape.
0
0





















